Integrating your SaaS product with Salesforce is no longer optional; it’s a must-have for enterprise deals, customer success teams, and smooth user experiences. But the actual integration can feel like tackling a three-headed beast: APIs, OAuth, and syncing models. This step-by-step guide simplifies the process, helping both product teams and technical founders launch a seamless Salesforce integration.
Table of Contents
Why Should Your SaaS Product Integrate with Salesforce?
Salesforce is the most widely used CRM for B2B sales and account management.
If your product doesn’t integrate with it, you’re forcing your users into manual work.
Benefits of Salesforce integration:
- Automates data flow between systems
- Reduces manual data entry for users
- Enables real-time visibility into product usage
- Unlocks mid-market and enterprise sales
- Helps you stand out from competitors
Example:
A project management SaaS can push task completion stats into Salesforce, allowing sales reps to view client onboarding health directly inside the CRM.
What Can You Sync Between Your SaaS Product and Salesforce?
Before jumping into APIs, define what you want to sync.
The most common data entities are:
| SaaS Data (Your Product) | Salesforce Object |
|---|---|
| Users | Leads or Contacts |
| Companies | Accounts |
| Transactions | Opportunities |
| Product Usage Events | Custom Objects |
| Support Tickets | Cases |
Tip: Use a planning doc to map each data type to its corresponding Salesforce object.
What Type of Salesforce Integration Should You Choose?
Salesforce supports different integration patterns:
1. REST API Integration
Most popular. You send and receive data using Salesforce’s REST API.
2. AppExchange App
You build and publish an app that customers install into their Salesforce instance.
3. Salesforce Connect
Allows real-time access to external data sources using OData—good for viewing, not editing.
4. Middleware (e.g., Zapier, Workato)
Fastest route to MVP integration, but limited flexibility.
| Type | Speed to Deploy | Flexibility | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| REST API | Medium | High | Custom needs |
| AppExchange App | Low | Very High | Enterprise |
| Salesforce Connect | Medium | Medium | Read-only data |
| Middleware | High | Low | MVP stage |
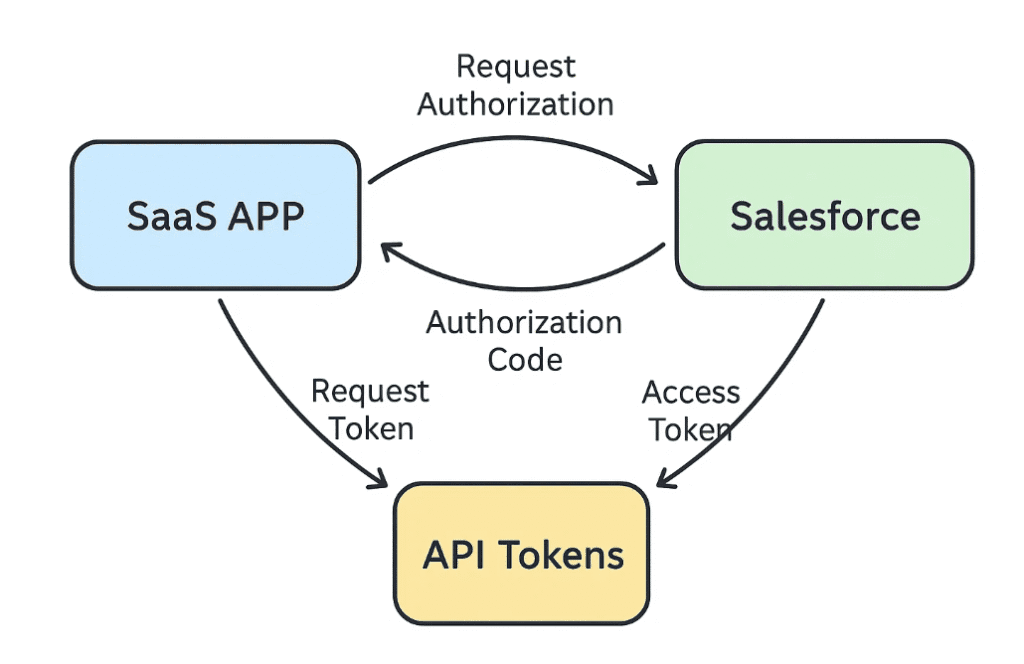
How Do You Authenticate with Salesforce?
Salesforce uses OAuth 2.0 for secure access. It ensures your product can act on behalf of the user without storing passwords.
Authentication Flow:
- Your app redirects the user to the Salesforce login
- Salesforce asks for permission
- Upon approval, Salesforce sends you an authorization code
- You exchange the code for an access token
- Use the access token to call Salesforce APIs
Tip: Use the Web Server OAuth Flow for SaaS products with backend servers.
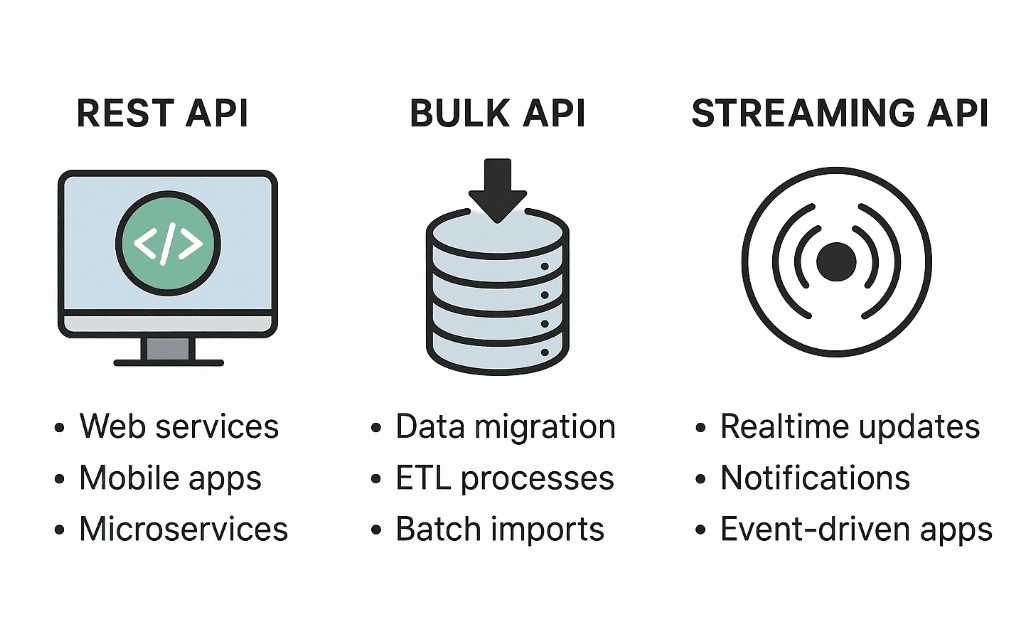
Which Salesforce APIs Should You Use?
Salesforce offers several APIs. Here’s when to use which:
| API | Use Case |
|---|---|
| REST API | Most CRUD operations on standard objects |
| Bulk API | Handling large volumes of data |
| Streaming API | Real-time updates with push notifications |
| Metadata API | Deploying config like custom fields |
Example:
If you want to update account details after a user upgrades their plan, use the REST API.
How Do You Map Your Data to Salesforce Fields
Your internal data structures probably won’t match Salesforce’s 1-to-1.
Here’s how to handle it:
- Create custom fields in Salesforce when needed
- Use external IDs for matching records
- Normalize values (e.g., format phone numbers or countries)
- Use lookup relationships to preserve parent-child hierarchies
| SaaS Field | Salesforce Field |
|---|---|
| company_id | Account.External_ID__c |
| plan_type | Account.Plan__c |
| last_active | Contact.Last_Activity__c |
Pro Tip: Use a data dictionary to maintain mapping consistency.
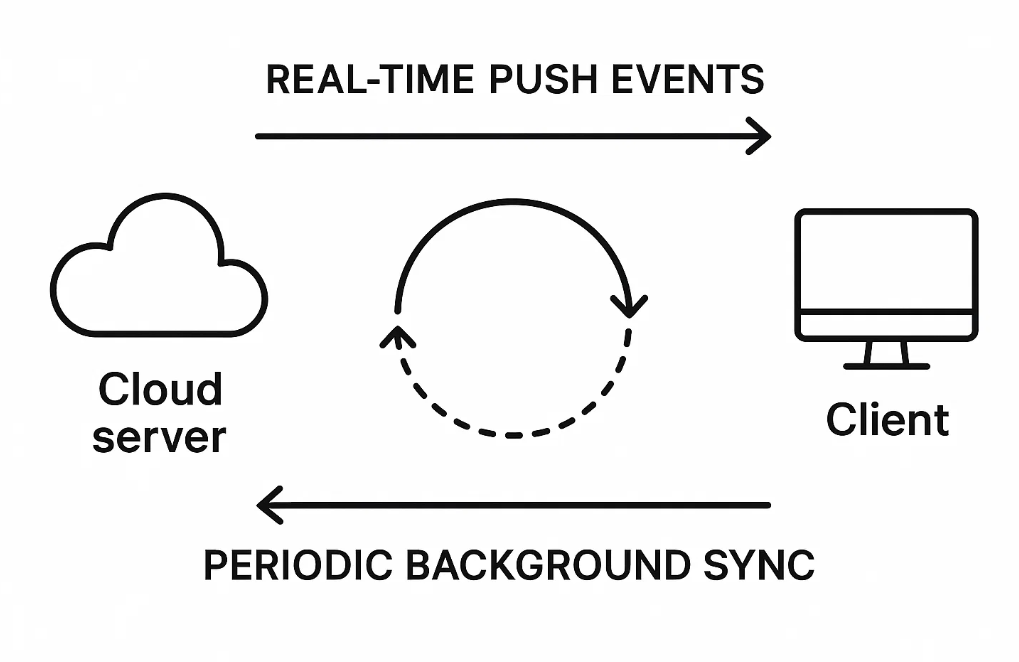
How Do You Handle Data Sync and Webhooks?
There are two key models:
1. Push Model (via Webhooks)
Your SaaS pushes data to Salesforce when something changes (e.g., new signup).
2. Pull Model (via Scheduled Jobs)
Your service fetches data from Salesforce at intervals.
Best Practice: Combine both.
- Use webhooks for real-time events
- Use scheduled syncs for backup or missed events
Example:
User signs up → webhook sends data to Salesforce.
Nightly job runs → checks for any missed records and updates Salesforce.
How Do You Manage API Limits and Errors?
Salesforce enforces daily API limits. Ignoring this can break your integration.
Solutions:
- Batch data when using the Bulk API
- Retry on failures using exponential backoff
- Log and alert on sync issues
- Use composite API calls to reduce roundtrips
| Error Type | Suggested Handling |
|---|---|
| 429 Rate Limit | Refresh the OAuth token |
| 400 Bad Request | Retry after the wait period |
| 401 Unauthorized | Refresh OAuth token |
| 500 Server Error | Retry with backoff |
Image Suggestion:
Error-handling flowchart with retry, logging, and fallback steps.
How Do You Test Your Salesforce Integration?
You don’t want to test on a client’s real data.
Use a Salesforce Developer Sandbox:
- Free for all developers
- Mirrors production environment
- Let you test safely
Testing Tips:
- Test all CRUD actions: create, update, delete
- Test with bad data to see how your integration fails
- Validate field mappings and workflows
Pro Tip:
Use tools like Postman, Workbench, or Insomnia to test your Salesforce APIs manually.
How Do You Package Your Integration for End Users?
Once it’s working, make it easy for customers to activate.
3 Options:
- Native Integration UI
Settings page in your app where users can connect their Salesforce account. - AppExchange Listing
Formal listing users install from Salesforce’s app store. - API Key Setup
For custom installs with technical guidance.
Tip: Offer guided setup with tooltips and in-app walkthroughs.
How Do You Keep the Integration Secure?
Salesforce data is sensitive. Don’t cut corners.
Security Best Practices:
- Encrypt access tokens and sensitive payloads
- Use short-lived access tokens
- Set API scopes to only what’s needed
- Rotate client secrets regularly
- Monitor access logs for anomalies
Reminder:
Any breach on your end could expose customer CRM data.
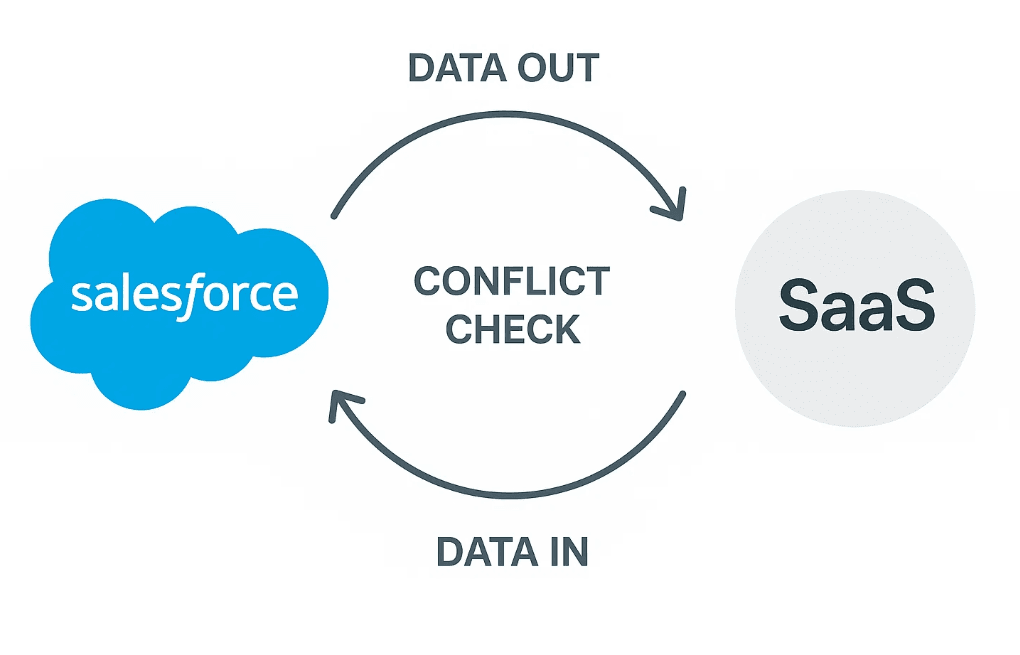
How Do You Monitor and Maintain the Integration Over Time?
Salesforce updates its API versions annually. Your integration must evolve.
Ongoing Maintenance Tasks:
- Monitor API deprecation notices
- Test your integration against new API versions
- Maintain logging dashboards for sync issues
- Allow users to re-authenticate easily
- Provide alerts when syncs fail or APIs hit limits
Example:
If your integration relies on a deprecated field, future Salesforce updates may break it—without notice.
Final Thoughts: Should You Build or Buy Your Salesforce Integration?
If Salesforce integration is a core selling point, build it in-house.
But if it’s just a nice-to-have, start with tools like Zapier or Workato to validate the need.
| Criteria | Build In-House | Use Middleware |
|---|---|---|
| Custom data mapping | ✅ | ❌ |
| Real-time sync | ✅ | ⚠️ |
| Enterprise readiness | ✅ | ❌ |
| Fastest to market | ❌ | ✅ |
TL;DR – Salesforce Integration Checklist
| Task | Done? |
|---|---|
| Define use cases & data mapping | ☐ |
| Choose integration type | ☐ |
| Set up OAuth 2.0 authentication | ☐ |
| Use Salesforce REST/Bulk APIs | ☐ |
| Handle sync logic & retries | ☐ |
| Build user-friendly setup UI | ☐ |
| Monitor errors and API usage | ☐ |
| Test in Salesforce sandbox | ☐ |
How Do You Set Up a Bi-Directional Sync with Salesforce?
Many SaaS teams only push data to Salesforce, but what if your customers also want to pull data from Salesforce into your app?
This is where bi-directional sync comes in. It allows both systems to stay updated and consistent.
Use Cases for Two-Way Sync:
- Syncing contact info if it has changed in Salesforce
- Pulling opportunity stage changes into your product
- Keeping user roles or account owner fields aligned
How to Do It:
- Push from SaaS → Salesforce:
Use webhooks or events in your app to trigger API calls to Salesforce. - Pull from Salesforce → SaaS:
Use the Streaming API or Change Data Capture to get notified when records are updated in Salesforce. - Conflict Resolution:
Decide which system is the “source of truth.”
If both systems update the same field (e.g., name or email), choose one to overwrite or log for review.
Best Practice: Timestamp all updates and sync based on “last modified” value.
How Do You Handle Custom Salesforce Configurations?
Every Salesforce org is different. Some companies have 100+ custom fields, while others rename standard objects entirely.
Common Customization Challenges:
- Renamed field labels (e.g., “Accounts” → “Organizations”)
- Required custom fields that block record creation
- Validation rules you didn’t account for
- Custom workflows that trigger upon data sync
Solutions:
- Use Salesforce’s Metadata API to fetch the schema dynamically
- Allow customers to map your fields to their fields inside a settings UI
- Run a configuration scan after OAuth is completed to detect field mismatches
- Use try/catch logic in your API calls to capture errors and provide fallback behavior
Example:
If your SaaS pushes anAccountbut the client requires a customRegion__cfield, your API call will fail unless that field is included.
How Can You Build a Field Mapping Interface for Non-Technical Users?
Your users shouldn’t need a developer to set up their integration.
A clean UI for field mapping will reduce support tickets and increase adoption.
What to Include:
- Dropdowns to select Salesforce fields
- Descriptions for each field (tooltips help)
- Auto-detection of required fields
- Test the connection button after mapping
- Save & preview option to simulate sync
Bonus Tip:
Show sample data next to each mapping so users can visually confirm accuracy.
| Your Field | Salesforce Field | Example Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Name | Contact.Full_Name__c | “Alice Johnson” |
| Company | Account.Name | “BrightTech” |
| Plan Type | Account.Plan__c | “Enterprise” |
How Do You Enable Account-Based Permissions for Salesforce Sync?
In many SaaS apps, not every user should have Salesforce integration rights. You need granular permission settings.
Add These Controls:
- Only admins can enable/disable Salesforce sync
- Let admins control which roles or users can map fields
- Option to scope sync at workspace/team/account level
- Audit logs to track who modified Salesforce settings
Real-world Scenario:
A client’s CSM accidentally disconnects the integration. Without audit logs, you won’t know what happened or who did it.
Backend Implementation Tips:
- Use feature flags (
salesforce_integration_enabled) - Store user role mapping in your database
- Implement scoped API tokens per account, not per user
How Do You Price or Package Salesforce Integration?
Salesforce integration is often a premium feature. Positioning it correctly can unlock more MRR from enterprise clients.
Pricing Models:
| Model | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Tier | Only available on Pro or Enterprise plan | Monetizing big clients |
| Add-on Fee | Extra monthly charge for Salesforce sync | Usage-based pricing |
| Free Feature | Offered to everyone to boost product stickiness | Low-churn strategy |
Tip: If you’re unsure, start with gated access, then monitor adoption. You can always expand access later.
What Analytics Should You Track Post-Integration?
Salesforce integration should improve product usage and reduce churn, but only if you measure it.
Key Metrics:
- Number of connected Salesforce orgs
- Frequency of data syncs
- Sync error rate
- Time to first successful sync
- Feature usage before and after integration
- Conversion rate from free trial to paid after enabling sync
Hope this will help you: https://youtu.be/Z5tcHCO6g84?si=JoNNdW6K9BSlC6at
Insight:
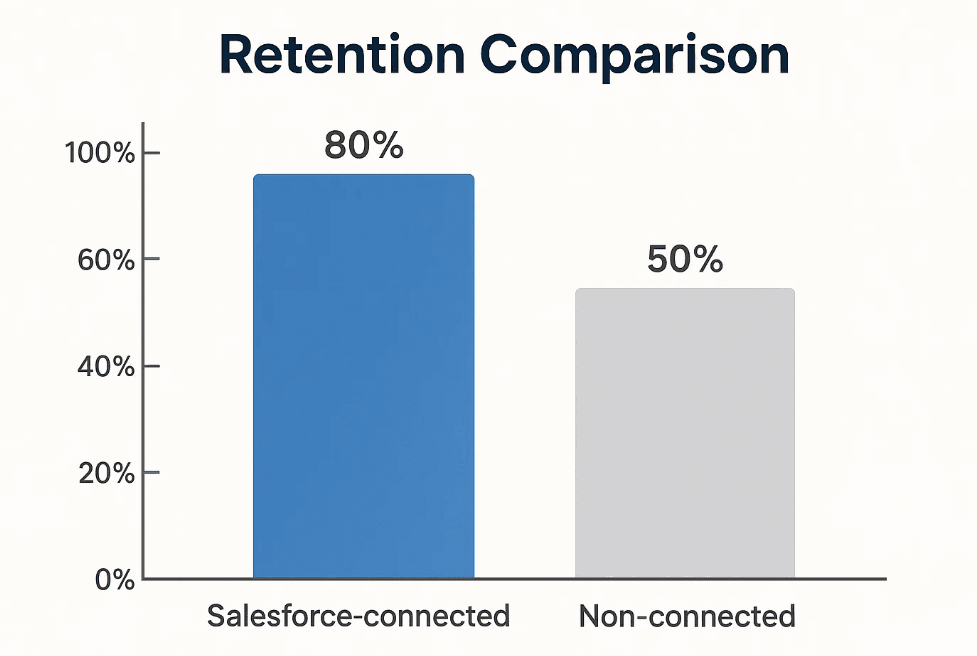
If Salesforce-connected users have a 30% higher retention rate, that’s a strong upsell signal.
Tool Suggestions:
- Segment or Mixpanel for event tracking
- Custom logs with sync outcomes
- Webhooks for failed sync alerts to Slack or Opsgenie
How Can You Win More Sales Demos with Salesforce Integration?
Marketing the Salesforce integration can be a game-changer for pipeline growth.
Here’s What to Do:
- Add “Salesforce Integration” to your homepage feature list
- Create a demo video walking through the integration
- Publish a dedicated landing page targeting the Salesforce keyword
- Ask your sales team to mention it in every enterprise pitch
- Include integration stats in your investor pitch deck
Example:
“Teams who enable our Salesforce sync see a 2x increase in onboarding success rate.”
Conclusion
Integrating with Salesforce isn’t just a technical task—it’s a product growth strategy. Whether you’re enabling better sales workflows or unlocking enterprise deals, a well-executed integration helps your SaaS product become truly sticky inside your customer’s CRM.
Done right, it boosts retention, improves upsells, and sets your product apart in a competitive market.
Next Steps?
Build a small proof of concept, test it in a sandbox, and slowly roll it out to early adopters.
You might also like:


